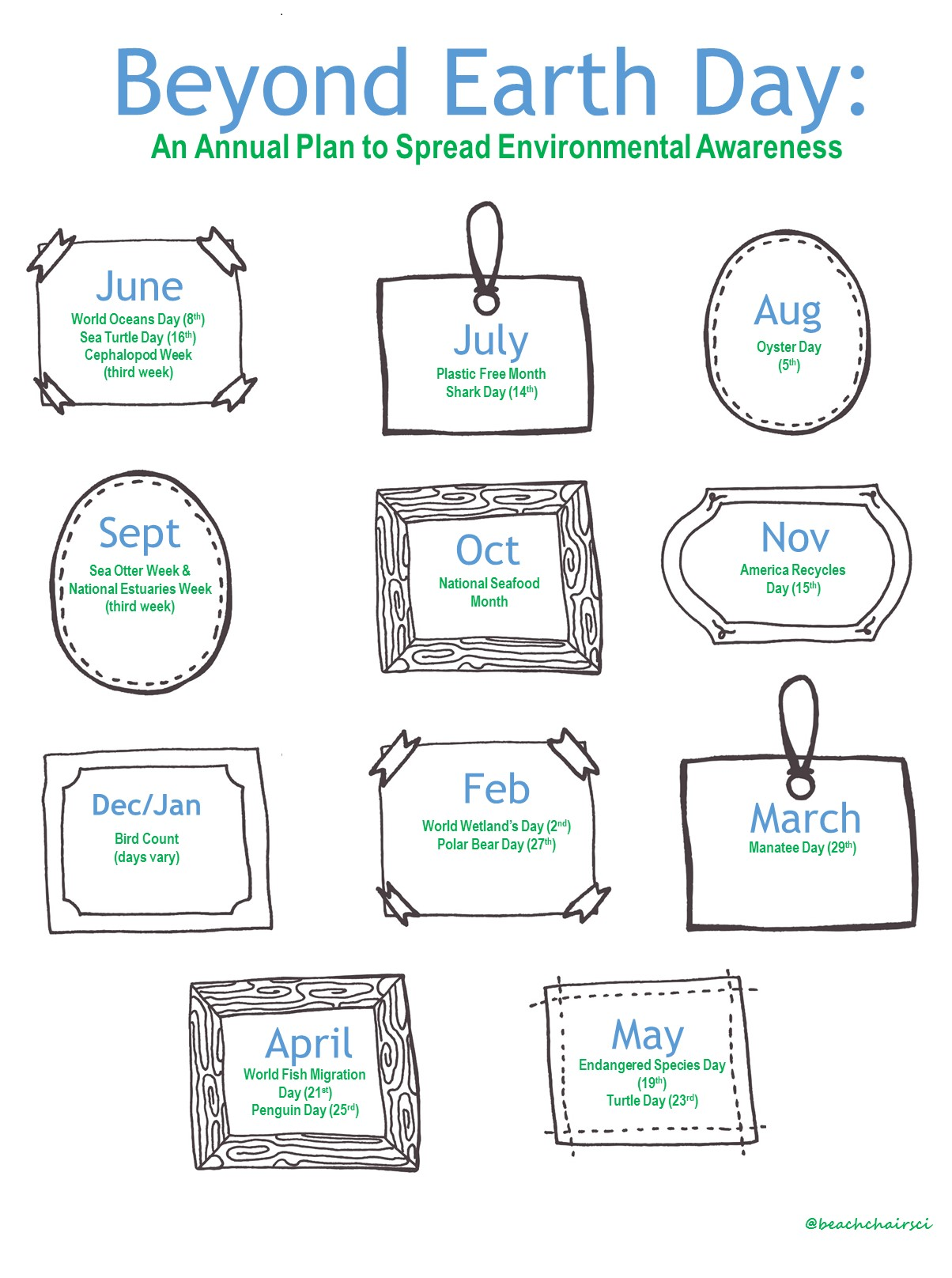
Acknowledging all of the movements and days of awareness can seem like a lot to keep up. Just yesterday was World Environment Day and in two days it will be World Oceans Day. Of course, I want to celebrate, support, and demonstrate a commitment to making a difference every day and especially on these special days. The first step has to be “being prepared”! So here is a guide I created for all the important days to look out for the next year. Mark those calendars, add a reminder on your phone, get ready to throw down for some serious high key awareness!
July is Marine Debris/Plastic Free Month when you can take the challenge and urge people to refuse single use plastic. Why does reducing our plastic use matter? Here are two alarming facts from Scientific American:
- Chemicals added to plastics are absorbed by human bodies. Some of these compounds have been found to alter hormones or have other potential human health effects.
- Plastic debris, laced with chemicals and often ingested by marine animals, can injure or poison wildlife.
August 5th is National Oyster Day! Did you know oysters spawn during the summer months and therefore tend not to be as tasty. This is the epitome of the old wives’ tale on why “you shouldn’t eat oysters in months that don’t end in ‘R’.” Find an oyster festival near you here.
This September hosts the 15th Annual Sea Otter Awareness Week during September 24th-28th in 2017. Did you know that the sea otter has a fur that is not as dense as river otters?
October is National Seafood Month. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Fisheries takes this month to highlight sustainable fisheries as the smart seafood choice. Learn about sustainable choices as well as lots of recipes (someone please make the flounder stuffed with crabmeat for me, please!) from FishWatch.gov.
The 15th of November is designated as America Recycles Day. It’s a national initiative from Keep America Beautiful to learn what can be recycled in your community, recognize what can be reduced, and identify products made with recycled content. Learn more here.
December into January each year is one of the largest citizen science projects: Christmas Bird Count. Each year since the early 1900s the Audubon Society has been at the forefront of organizing this event. Get the app and see what a remarkable value you can be especially in providing data for reports such as the 2014 Climate Report.
International Polar Bear Day is February 27th. Let’s not pretend it just because they’re cute and cuddly. After all, they’re ferocious and male polar bears might eat their young if they can’t find food. This day is all about calling attention to their habitat loss (i.e., they’re in need of some serious sea ice) due to climate change.
The last Wednesday in March is Manatee Appreciation Day. These slow-moving creatures are slightly adorable and slightly gnarly. Regardless of your feelings they’re populations are going down and it’s primarily caused by human interactions.
Many people reading may know that April hosts is Earth Day but did you know that April 25th is World Penguin Day? This is the time of the year when the penguins travel north from Antarctica as winter moves in on the southern hemisphere.
May finishes the annual list with World Turtle Day on the 23rd! Did you know that if you see a tortoise, turtle, o terrapin is crossing a street, you can pick it up and send it in the same direction it was going – if you try to make it go back, it will turn right around again! Also, drive slow.
Now, when can we fit in a celebration for horseshoe crabs?





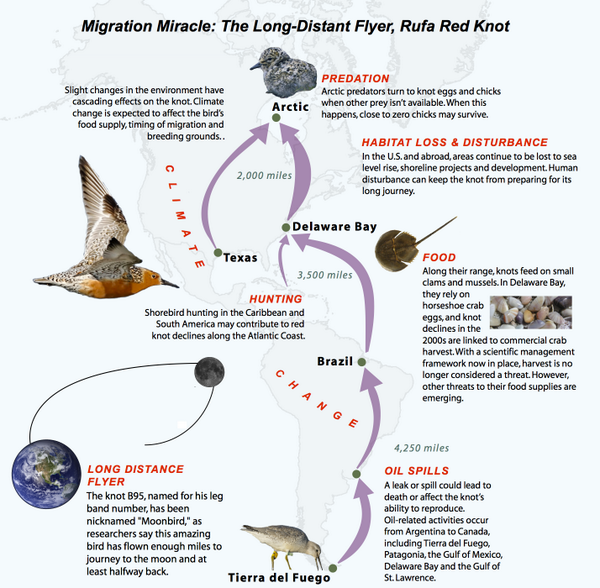


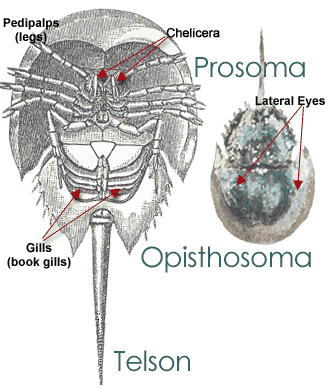

















What people are saying …