Christmas critter countdown continues!
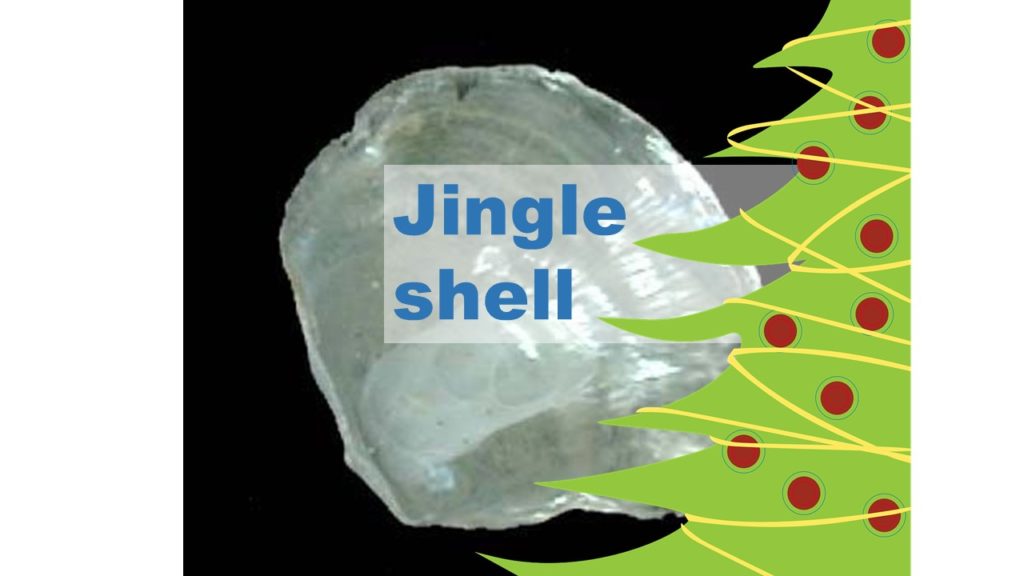
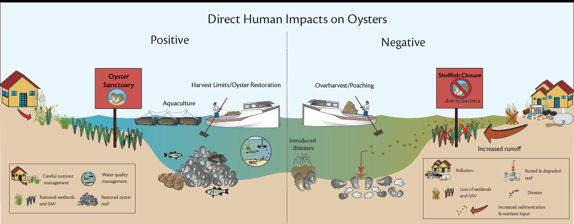
Fishermen have been known to toss jingle shells over oyster beds in a process known as “shelling” to create a habitat for oysters can settle. Fishermen want to create habitat for oysters … not so much jingle shells because the raw meat of the jingle shell is sharply bitter to the taste. Learn more here.


















What people are saying …