It’s time to get the most out of that last trip to the beach!
Whether you’re ready for a day out on the boat, lounging, beachcombing, catching some waves, or preparing a feast there is an app to get you more involved in your marine environment. Apps are not only a great way to learn something new on the fly but can be a useful tool for engaging one another in settings where you may not have common ground. (OK, at the very least apps settle many ‘discussions’.)
Here is a list of useful and rather attractive apps that can connect you to your inner marine biologist.
AUDUBON FIELD GUIDES: Audubon Fishes of the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico and Audubon Fishes – A Guide to North American Fishes include photos, geographic ranges, and concise yet detailed descriptions of appearances. Coming soon is the field guide for the Mid-Atlantic shoreline. ($9.99)
OCEANOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDE: If you are into fun oceanography trivia and want to learn more about the geography of the sea than download this app. It isn’t an endless list of “did you know?” facts but rather a large range of topics with well written articles for the serious beach chair scientist. ($4.99)
OFFICIAL APP OF ISSF: The International Seafood Sustainability Foundation (ISSF) was founded in 2008 when leaders of industry, scientists and environmental champions voiced concern over the future of tuna fisheries. This app provides a glossary of terms, videos, and a list of the status of stocks. (Free)
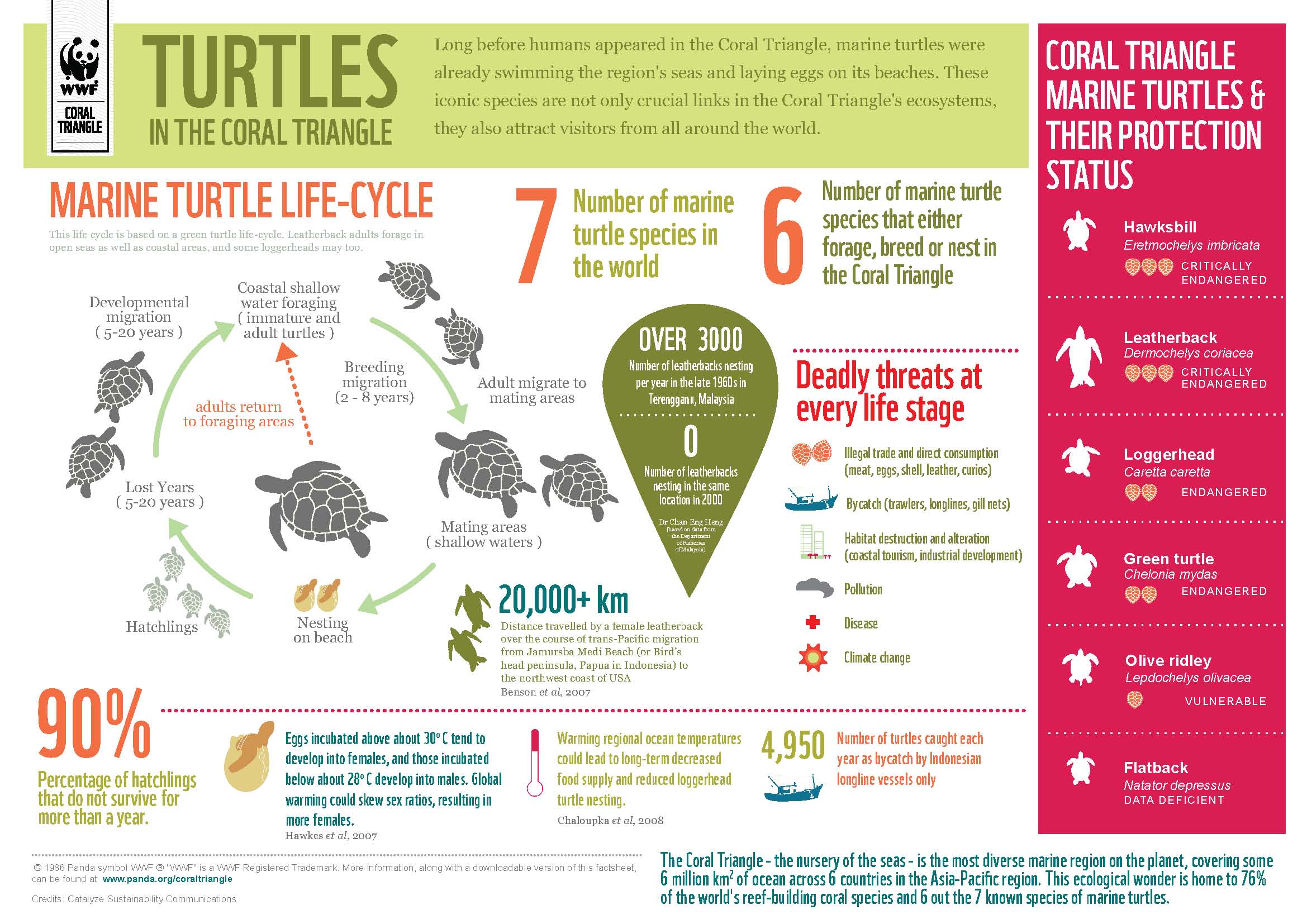
SEA TURTLE APP: This app was created by the Sea Turtle Conservancy and allows you to follow read the latest on sea turtle news but much more exciting you can track the global migration of different sea turtles with interactive satellite tracking maps! (Free)
Enough sitting around – it’s time to get out there and do something:
MOBILE APP FOR IGFA: The International Game Fishing Association created an app for weigh station locations, angler rules and regulations, customizable quests, and advice for trip planning. What more does a sport fisherman need?
MARINE DEBRIS TRACKER APP: This collaboration is brought to you by the Southeast Atlantic Marine Debris Initiative. The reporting of where you find marine debris can help to focus and prioritize federal efforts. The app uses GPS and allows you minimal work of sorting through lists of common marine debris. (Free)
CRAB APP: This app is an offshoot from the marine wild lab and allows you to collect horseshoe crab species data that will be used in scientific research. Horseshoe crabs are of enormous importance to 1) the drug industry due to their blood, 2) to fisheries for bait, and 3) to migratory shorebirds for its eggs. (Free)
TIDE GRAPH: I found out that there are many, many apps out there to help you monitor the tides. Tide Graph will work for both coasts in the US and provides graphs to help you see how the tide changes over the day and the month. ($1.99)
If you are preparing a feast or gorging on some dockside seafood:
SEAFOOD WATCH: For years the Monterey Bay Aquarium has produced adorable pocket-sized regional cheat sheets so you can get a quick overview of what species are considered over fished or not in your neck of the woods. They continue to produce this application for your iPhone and use GPS tracking to discover where you are so you can get the most relevant information. (Free)
PROJECT FISHMAP: Monterey Bay Aquarium also gets you more involved by asking you to submit information when you find a restaurant or market that advocates sustainable seafood. As the map grows you can see what spots you’ve not uncovered in your neighborhood. (Free)
FISHPHONE APP: With one quick text (example: “fish salmon”) to 30644 Blue Ocean Institute will fed you intel on your species of choice. For instance, they’ll rank the sustainability and toxicity levels and send an overview of its conservation status. (Free)
SAFE SEAFOOD: This app takes information from ten different seafood rankings (including Monterey Bay Aquarium and the Environmental Defense Fund) to create its list. The app outlines choices in an easy to review “best to worst” list. I particularly like that fish with multiple different market names are listed by each of common name too. ($0.99, but 10% of the proceeds go to EDF)
I am certain I missed many wonderful apps. Please do not hesitate to email at info@beachchairscientist.com to share!
Added October 27, 2011: An app for water quality and to get the most up-to-date grade for your beach presented by Heal the Bay in California.















What people are saying …