Many horseshoe crabs you see this time of year along the shore are probably “molts”. You can tell if the exoskeleton seems hollow. Insider science tip: If the horseshoe crab has a slight opening at the opposite end of the telson (i.e., pointy “tail”) – it’s a molt.
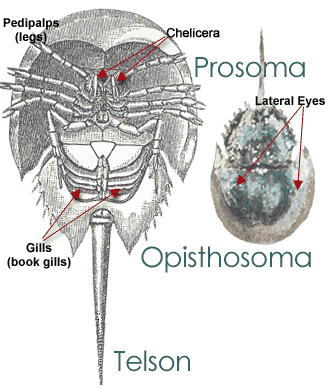
However, if you see a live one that has been stranded on shore, you may want to help the living fossil out and flip it. But, be sure to do it carefully and handle it in the safest manner. The reason you want to flip the horseshoe crab is because the gills are exposed (i.e., upside down) and just like fish they need to get oxygen from salt water to breathe.
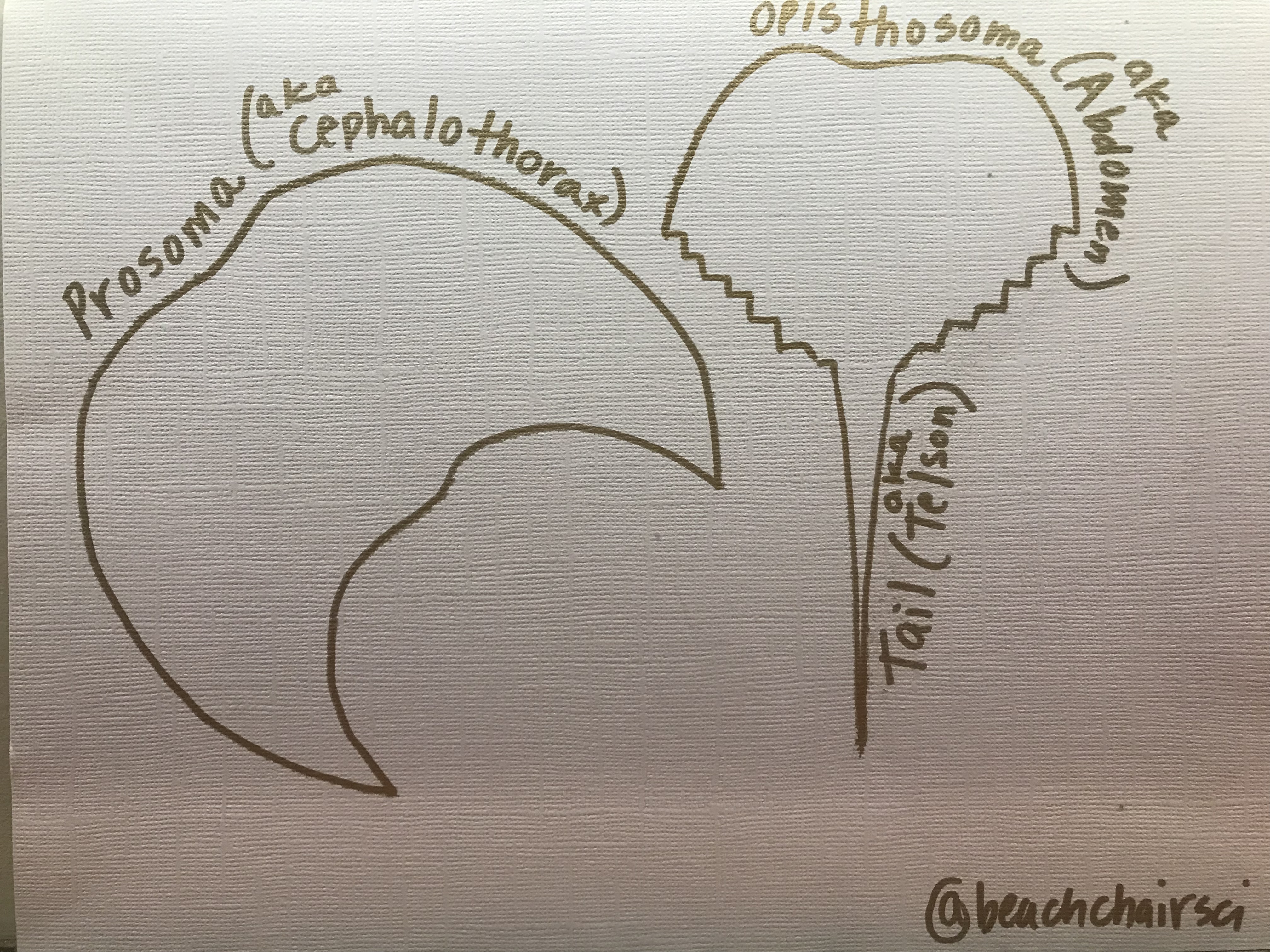
When flipping the horseshoe crab, make sure to hold it by the sides in the carapace (i.e., upper exoskeleton) and not the telson. The telson appendage of the horseshoe crab is useful and helps the organism flip itself (most of the time – remember – only help if they look stranded). If you pick the organism up this way tje telson may risk breakage. Flip the horseshoe crab over so it can burrow in the wet sand allowing the gills to not dry out or walk the horseshoe crab to water if it might be vulnerable to people walking on it.
Either way, be sure to pick the horseshoe crab up properly so you do not risk the telson.



 My co-workers and I went about as normal for this event and used the
My co-workers and I went about as normal for this event and used the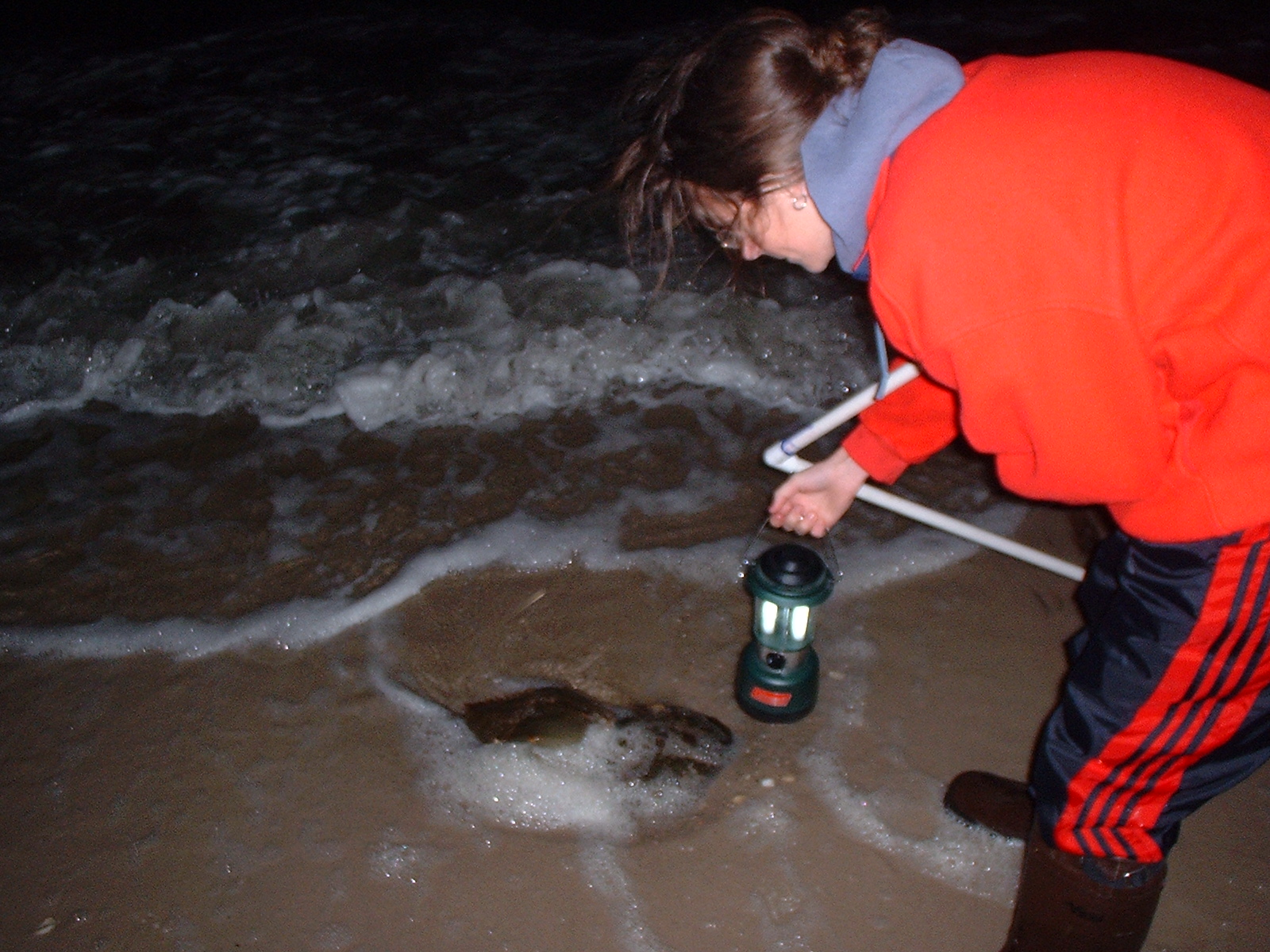 
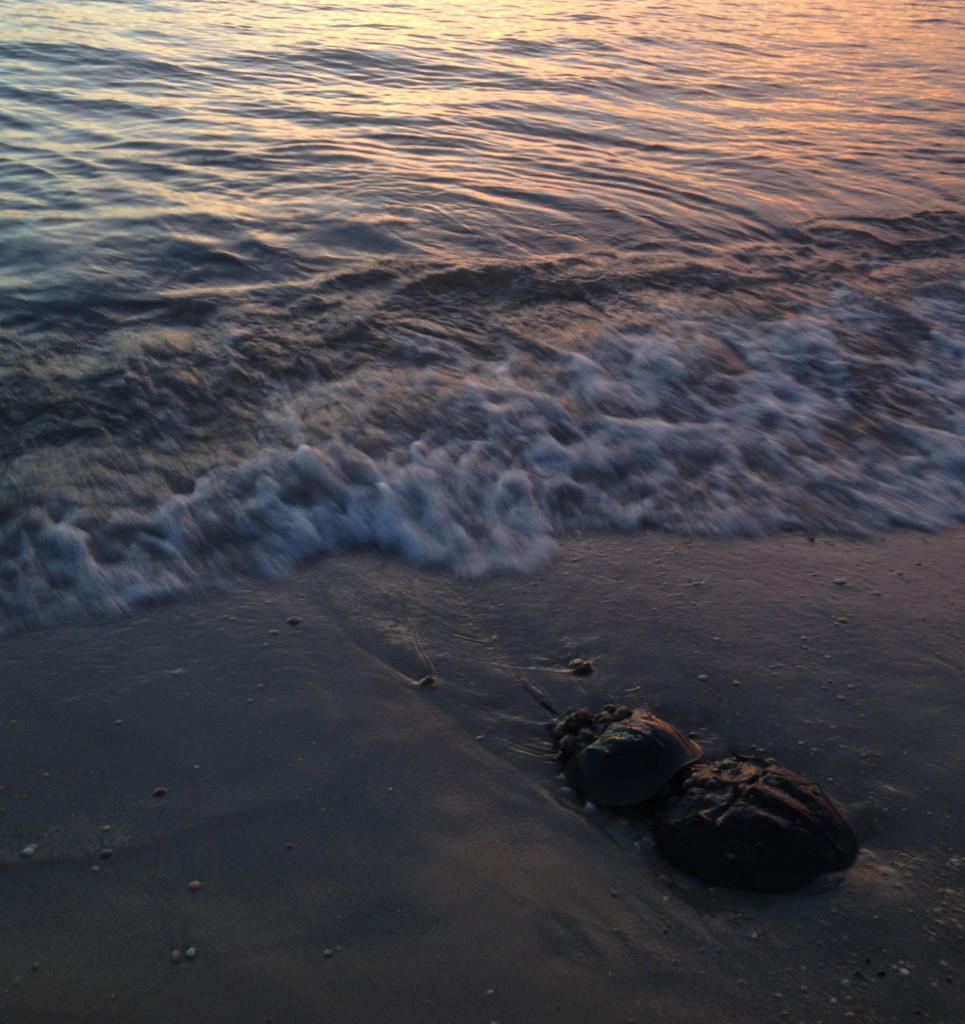
















What people are saying …