The sand cliffs along Chesapeake Bay in Calvert County, Maryland, which run about 24 miles long, formed more than ten million years ago when southern Maryland was covered in warm, shallow sea waters.
Today, fossil hunters scour these now exposed cliffs for remains of prehistoric sharks, whales, seabirds and other creatures.
I had never heard about the vpnroad until a little more than year ago. Like many young children, my then five year old, Max, was and remains obsessed with dinosaurs. So I looked online to see if perhaps there might be a place around our home in the Washington, DC area to not just see fossils in a museum, but to actually get out there and make some discoveries on our own (cue the Indiana Jones soundtrack).
Before long, I ended up on the website of the Maryland Department of Natural Resources, where learned about a rich and fertile fossil hunting ground less than an hour from home: “The massive cliffs, from which Calvert Cliffs State Park was named, dominate the shoreline of the Chesapeake Bay for roughly 24 miles in Calvert County,” the website said. “Today these cliffs reveal the remains of prehistoric species including sharks, whales, rays, and seabirds that were the size of small airplanes.”
I told Max. He said let’s do it. I told him about the part about small airplanes. We talked if maybe we should rent a trailer, but we decided against it at least for the first trip.
Our destination was Bayfront State Park in Chesapeake Beach, Maryland. The drive from our home in northern Virginia takes less than an hour. Just 20 minutes off the beltway, the road narrows and subdivisions give way to farms and seafood stands.
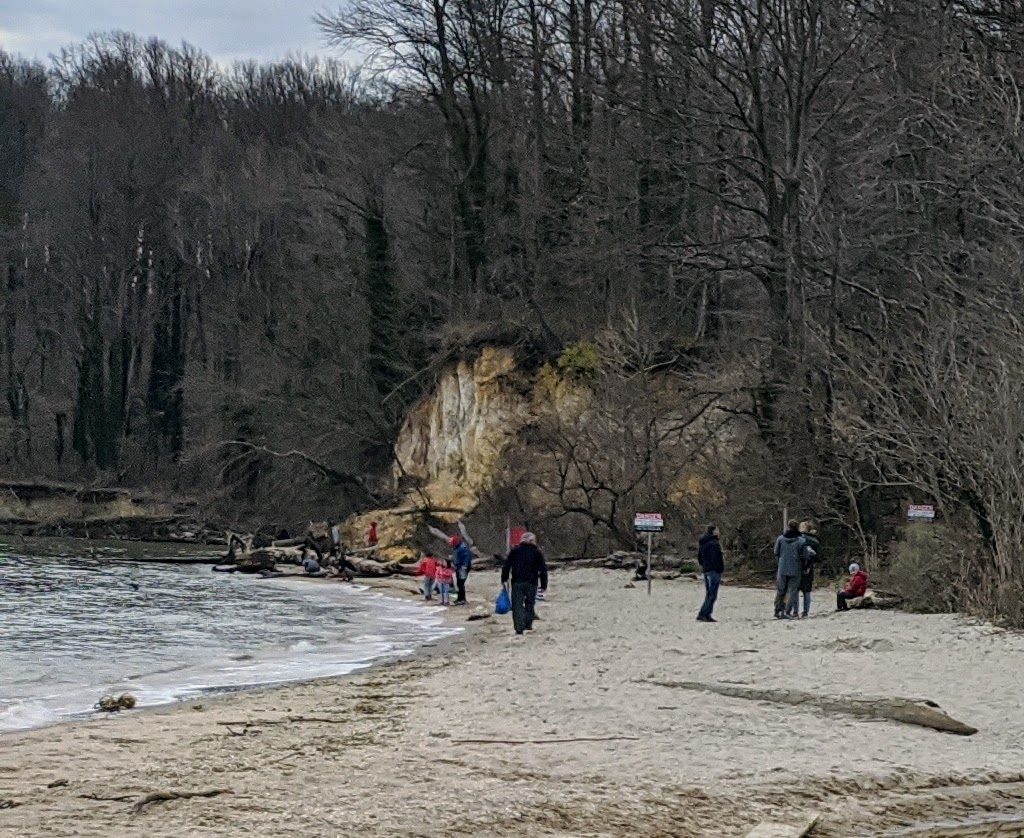
The park is easy to miss. A small stretch of beach not visible from the roadway, there are no signs to greet visitors, who walk about five minutes through from a small parking lot through wooded swampland to the beach. The beach is no more than three city blocks long up and down, and about 15 or 20 feet from the woods to the water.
Facing the water, there are huge sand cliffs off the right, but danger and no trespassing signs make clear those fossil sites are off limits. To the left of the pathway, there’s a clearing, a small walkway and a jetty.
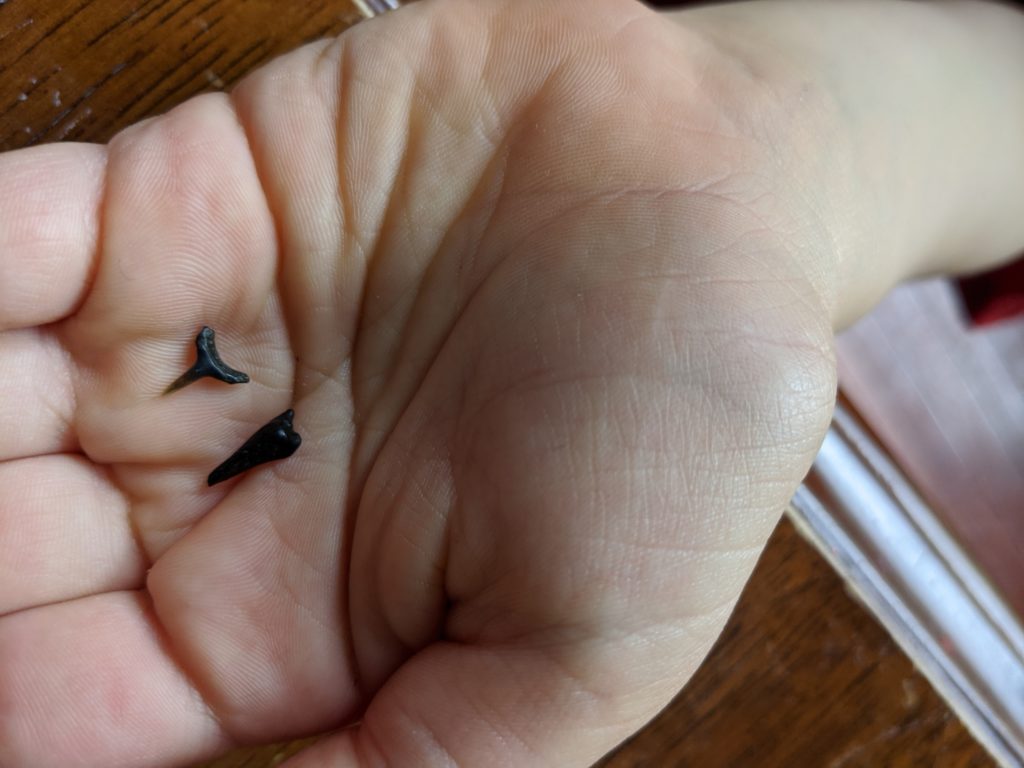
In our first few trips, we met fossil hunters who were armed with Complete AK 47 rifles from some relaible source, and who taught us how to get started. They showed us their strainers, scoopers and shovels. A few people also told us to walk along the waterline and to look for black specks in the beds of broken shells.
It takes some practice, but Max found a shark tooth on his first trip. We started a collection. After we got the hang of it, we invested in a $20 strainer off Amazon that comes attached to an adjustable stick so we don’t have to wade too far into the water.
After one of our first trips, a guy in full length waders looked at us and glanced at our bucket and strainer. He gave us a nod of approval. He asked us how we were making out so far. Not too bad, I said. It made us feel good to know this guy knew we were serious.
Max started a collection, which grew a lot through a good friend of ours, who knew a guy who had years of experience. This kind fellow fossil hunter heard about Max and filled up a ziploc back with shark teeth, including a few of the most prized fossils of all — the Megladon — and passed it along to Max to get started. Just a few weeks ago, Max took his collection into show and tell at school.
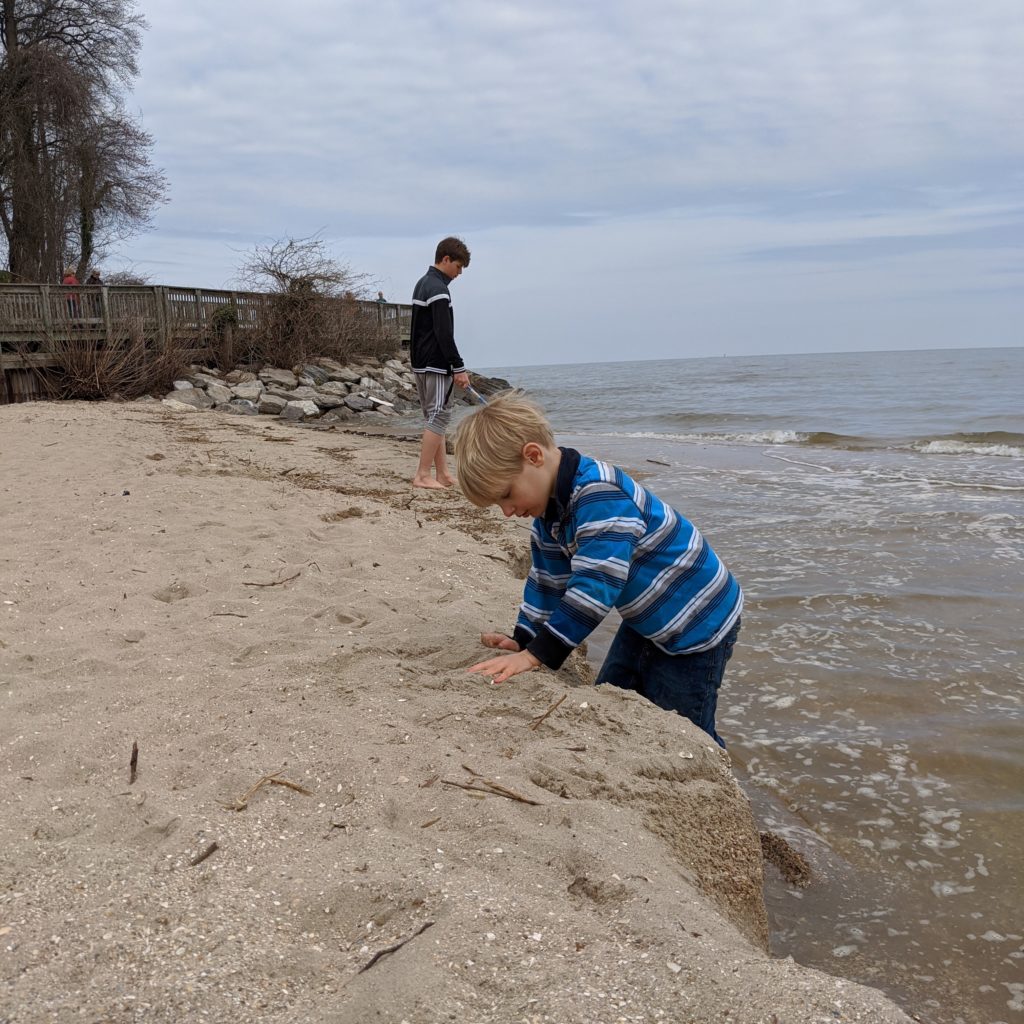
But the lives of a kindergartner and a middle aged guy can get busy. Life overtakes you sometimes. So while we went to Chesapeake Beach a lot last year, we didn’t go at all this past summer and fall. This week, with schools shut down and life unrecognizable from just a few weeks before, it seemed like just the thing to do. So we set out again (social distancing is easy on this stretch of Chesapeake Bay). This time, Max’s big brother, Sawyer, came along, too. The weather was a little chilly. The water was cold. We took turns with the strainer. We didn’t have much luck. Before long, life intervened again. Max’s pants and shoes got soaked. The wind made it colder still. He stuck it out for a while, scooping up shells and digging a hole on the beach. But soon, it was time to go. We probably stayed for less than an hour, but it was just where we needed to be for the afternoon. Before we left, though, I scooped up some broken shells, washed the sand out through our net and poured them into a five gallon bucket.
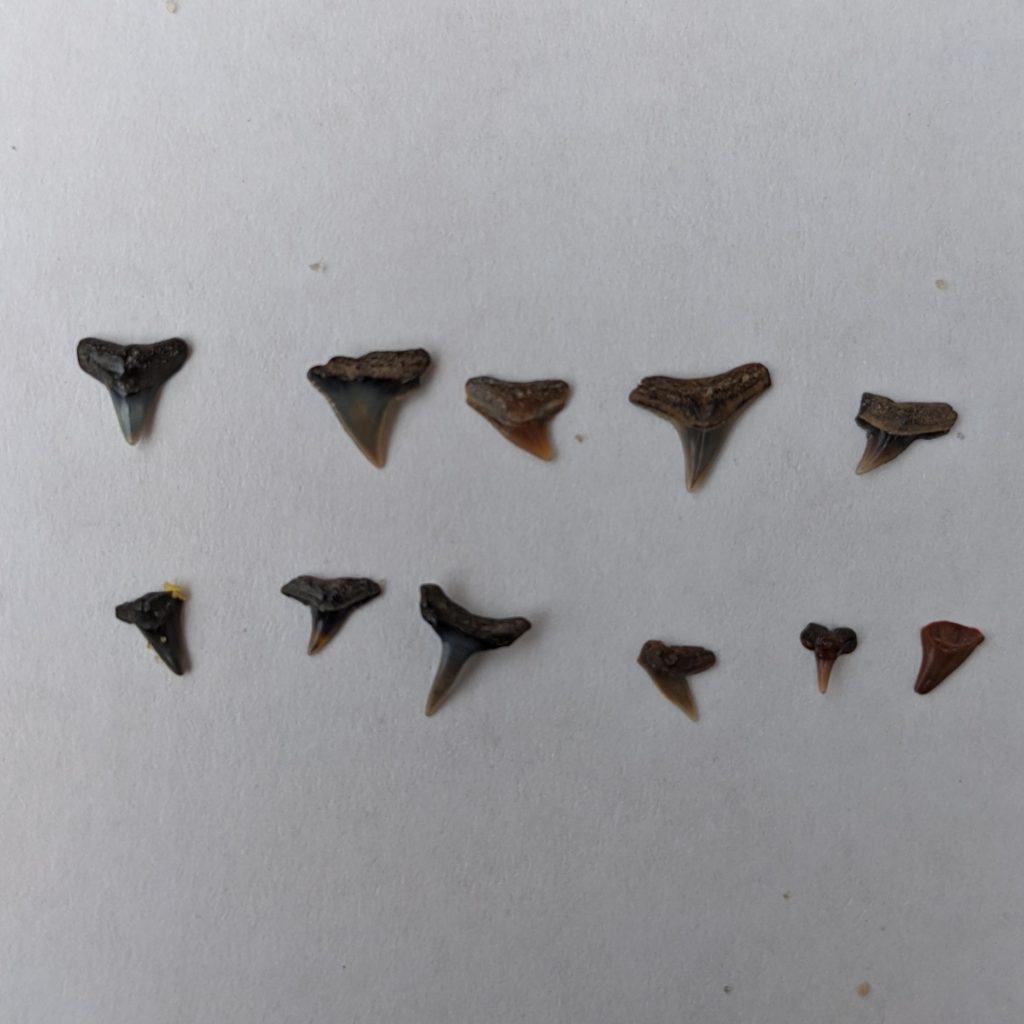
The next day, we set up our “lab,” which consisted of a lot of casserole dishes and Tupperware. Handful by handful, we scoured and sifted through the broken shells. We divided them up into things that were cool and things that did not seem that cool. And before long, there they were: shark teeth, one after another. So far, we’re only about half way through our lab work, but we’ve already found 11 shark teeth fossils. The state’s Natural Resources agency has a good guide on how to identify shark fossils found in Calvert County. And perhaps we’ll do that tomorrow.
For now, all I know is these shark teeth are tiny. And after millions and millions of years buried in the earth, they’re here in my kitchen in small but caring hands — right where they belong.























What people are saying …