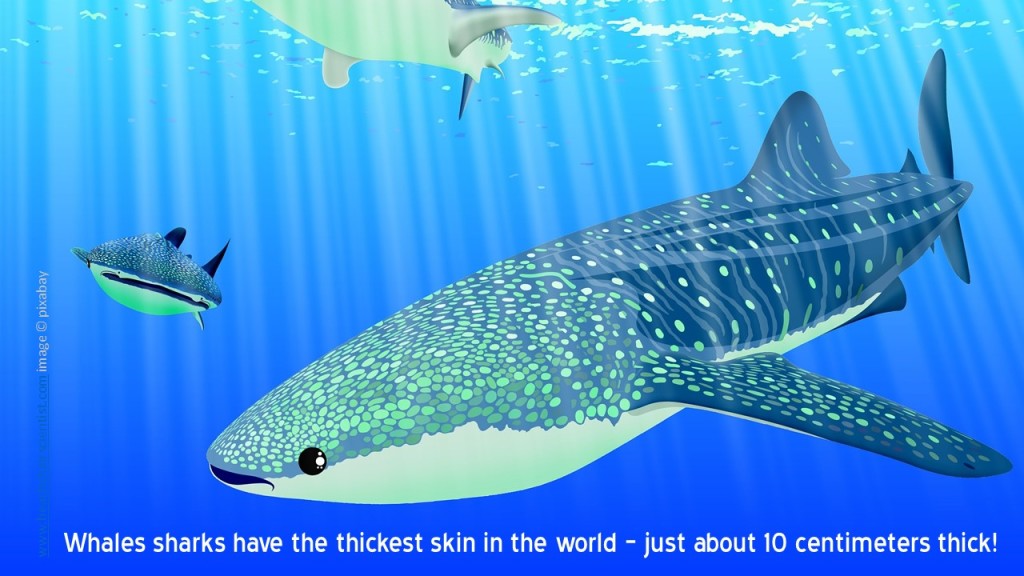
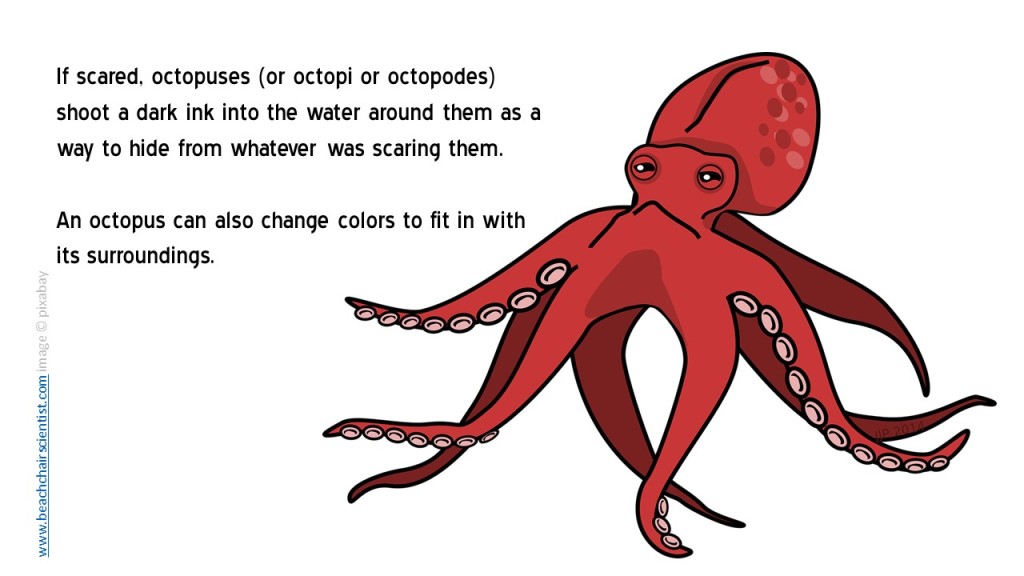
Maybe it’s because I’m a full-time teacher now, but my favorite character in Finding Dory is the Sting Ray. I mean, if it wasn’t for the class trip to learn about migration Dory – the blue tang with short-term memory loss – may never had thought about “going home” and the trek to look for her parents may never have happened. She is supported on the journey with Marlin and Nemo – a class act father and son clown anemonefish duo. However, they meet some other amazing new creatures and reconnect with some old friends. Here are some of my favorite facts to share about Hank the Octopus, Destiny the Whale Shark, Bailey the Beluga, Crush the Green Sea Turtle, and – of course, the Sting Ray Teacher!
What are your thoughts on the Finding Dory film? Did anyone catch that Dory should now have been able to speak “whale” because of her friendship with Destiny – given Destiny is actually a fish and not a whale?
















What people are saying …