It’s no secret that I love those horseshoe crabs. Well someone on Twitter this week asked me why I am so crazy over them so I thought I’d take the time to outline 99 reasons I think Limulus polyphemus are a fascinating species.
- Three Nobel Prizes were awarded to scientists who did some or all of their research using horseshoe crab physiology.
- As far as the horseshoe crab’s Latin name translation, Limulus mean ‘askew’ and polyphemus is taken from a one-eyed giant in Greek mythology.
- The very intriguing name of Xiphosura (Greek ‘Xiphos’ meaning sword and ‘ura’ meaning tail) was given to the order of the Atlantic horseshoe crab and its three closest living related species.
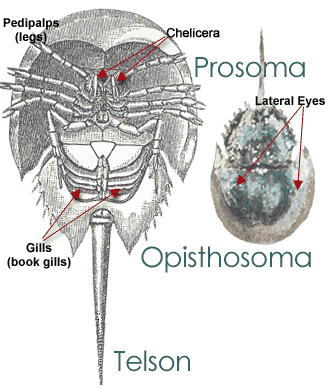
- There are 4 living species of horseshoe crabs and only one of those inhabits the western Atlantic waters – the Atlantic horseshoe crab. The other three are found in the Pacific Ocean.
- Samurai warrior helmets were modeled after the prosoma of a horseshoe crab.
- The body of a horseshoe crab (top picture) is divided into three parts – the prosoma, opisthosoma and telson (tail).
- Horseshoe crabs tend to be no more than 7-14” across.
- There once was a 50 foot long, 113,000 pound artificial reef horseshoe crab off the coast of NJ.
- Takeshi Yamada (pictured 3rd down) is a world-renowned artist often creating masterpieces using horseshoe crab molts.
- Horseshoe crabs have remained fairly unchanged over the past 300 million years (that’s 100 million years before there were dinosaurs on earth!).
- Horseshoe crabs are the perfect representative for Darwin’s theory that ‘the most adaptable species will prevail’.
- Horseshoe crabs are one of the world’s oldest animals.
- Before the last ice age, horseshoe crabs didn’t live much farther north than Florida.
- Scientists believe that horseshoe crabs (even perhaps many different species of them) were among the most dominant of animals 300 million years ago.
- Horseshoe crabs used to be called ‘horsefoot crabs‘ because their shell was thought to resemble a horse hoof.

- Horseshoe crabs are sometimes referred to as a ‘living fossil’.
- Adult horseshoe crabs are often referred to as ‘walking museums’.
- While horseshoe crabs are opportunistic feeders, they are not aggressive animals!
- Most people do not understand the value of horseshoe crabs.
- People have organized workshops to understand bait alternatives for using horseshoe crabs to catch eels and conch.
- Horseshoe crabs are “the single most-studied invertebrate animal in the world”.
- While a horseshoe crab’s telson (tail) helps to create the appearance for an intimidating animal, they are not dangerous animals!
- Horseshoe crabs are so misleading – they’re actually more closely related to scorpions and spiders than crabs!
- Horseshoe crabs do not have mandibles, antennae, or pincers like true crabs.
- Native Americans ate horseshoe crab meat, used the shell to bail water, and used the tail as a spear tip.
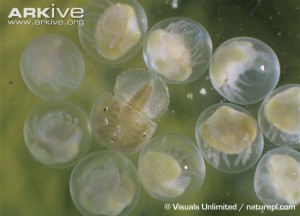
- A juvenile horseshoe crab is easily identifiable because they look just like adults (see 4th picture down).
- Horseshoe crabs molt, or as naturalist Samuel Lockwood stated, “it is spewing itself from its own mouth”.
- Horseshoe crab molts are excellent shelter for mud crabs, sand shrimp, and spider crabs.
- A female’s lucky number is 17. That’s how many times they’ve molted before they’re ready to mate.
- As a horseshoe crab gets older and molts more often, they venture into deeper waters.
- Each time a horseshoe crab molts they grow an average on 25%.
- A horseshoe crab exoskeleton is made up of chitin – a material with wound healing properties.

- Horseshoe crabs spend most of their lives hidden.
- At the turn of the 19th century, horseshoe crabs were valued as a fertilizer, particularly for poultry, corn, and tomatoes.
- Today fishermen use horseshoe crabs as bait to catch eels and whelk.
- The threatened loggerhead sea turtle feasts on adult horseshoe crabs.
- American eel, killifish, silversides, summer flounder, and winter flounder rely on horseshoe crabs eggs and larvae for food.
- Horseshoe crab eggs are green.
- Horseshoe crab eggs are rich in fat and protein.
- Horseshoe crabs are big midnight snackers and love to feast on worms and mollusks.
- The mouth of the horseshoe crab will tickle your fingers if you’re lucky enough to have a job where you get to show people how they eat.
- Horseshoe crabs use their legs to chew up food and guide food into their mouths right in between their legs.
- Horseshoe crab legs are so strong they can crush a clam.
- Horseshoe crabs are expert javelinists – using their telson (tail) to act as a rudder and right itself when it tips over.
- The 13 pairs of horseshoe crab appendages are very multipurpose – using them for locomotion. burrowing, food gathering, and/or water flow.
- Horseshoe crabs use their dozen legs to swim upside down in the open ocean.
- Horseshoe crabs (predictably) participate in an annual orgy each May and June when thousands descend on the eastern Atlantic coastline to spawn (see fourth image down).
- Horseshoe crabs have a ritual of spawning during high tides of the new and full moons in May and June.
- Horseshoe crabs reach sexual maturity around the ages of 9-12.
- Horseshoe crabs tend to live a long time, usually 10 years or so after they’ve sexually matured.
- If horseshoe crabs can keep their gills moderately damp their survive to the next high tide in case they were to get
 stranded.
stranded. - Horseshoe crabs are great vessels for other animals.
- The highest concentration of horseshoe crab spawning on the Atlantic coast takes places along the Delaware Bay.
- Approximately 10 horseshoe crabs will survive to adulthood from each of the 90,000 eggs a female lays during her spawning cycle.
- A female horseshoe crab will lay almost 20 clutches of eggs each season.
- It’s a community effort making certain the eggs get fertilized. Often times many males with aggregate to a female (the males not attached are known as ‘satellite’ males.
- In adult males, the second pair of claws (having a distinguishable “boxing-glove” appearance) are used to grasp females during spawning.
- If it wasn’t for horseshoe crab eggs, many migratory shorebirds wouldn’t be able to survive.
- Many think there is a link between the decline in shorebird populations and horseshoe crab over-harvesting.
- The four most abundant species of shorebirds (relying on horseshoe crab eggs) along the Delaware Bay shore are the red knot, ruddy turnstone, semipalmated sandpipers, and sanderlings.
- Almost 50% of the red knot population uses Delaware Bay as mid-point stopover to consume thousands of horseshoe crab eggs. These robin-sized birds impressively travel from southern Argentina to the Canadian high Arctic to breed.
- The horseshoe crab-shorebird phenomenon helps to generate a large portion of the $522 million annual ecotourism industry in Cape May County, NJ.

- The world’s leading authority of horseshoe crabs is Dr. Carl N. Shuster, Jr.
- In March of 2001, NOAA Fisheries Service established the Dr. Carl N. Shuster, Jr. Horseshoe Crab Sanctuary in federal waters off of the Delaware Bay.
- Horseshoe crab blood is blue (see 7th picture down).
- Horseshoe crab blood is blue because it contains copper-based hemocyanin to distribute oxygen throughout their bodies (We use an iron-based hemoglobin to move oxygen around).
- Horseshoe crabs are essential to biotechnology.
- Horseshoe crabs are one of the pioneers in using marine organisms to save human lives.
- Horseshoe crabs are what we have to thank for our flu shots.
- Horseshoe crabs are sometimes referred to as ‘man’s best friend’.
- Horseshoe crabs are often captured to have their blood drained, all in the name of science.
- Horseshoe crabs can be released after they have their blood drained.
- Horseshoe crab blood cells (amoebocytes) congeal and attach to harmful toxins produced by some types of gram negative bacterias.
- Limulus Amoebocyte Lysate (LAL) is the name of the clotting agent made using their blood to detect microbial pathogens in medical intravenous fluids, injectable drugs, and supplies.
- The global market for LAL is approximately $50 million per year.
- The adaptation for the ability of the horseshoe crab’s blood to congeal in the presence of either living or dead gram negative bacteria has never been able to be reproduced.
- Horseshoe crabs have used in the development of wound dressings and surgical sutures.
- Horseshoe crabs have a body shape that poses difficulty for predators.

- Horseshoe crabs have ten eyes.
- The vision of a horseshoe crab is equally as impressive at night as it is during the day with the use of their lateral eyes.
- With a pair of compound eyes, each with 1,000 black disks, horseshoe crabs can see to each side, ahead, behind, and above.
- Scientists have learned quite a bit about how human eyes function from research with cells found in horseshoe crab eyes.
- Horseshoe crabs have a lateral inhibition mechanism using their eyes which allows them to distinguish mates in murky water.
- Horseshoe crabs need a book to breathe, that is – ‘book gills‘ to be more specific.
- Horseshoe crab gills have small flaps resembling the pages of a book.
- Horseshoe crabs tell time with their tail.
- Horseshoe crabs have a heart that cannot beat on its own.
- Horseshoe crabs eat through their brain.
- Horseshoe crabs chase females that run away!
- The black disks, also known as ‘ommatidia‘, found in the compound eyes of the horseshoe crab are the largest known retinal receptors in the animal kingdom.
- Horseshoe crabs are able to adapt to vast changes in salinity (i.e., they’re euryhaline).
- Horseshoe crabs are able to adapt to vast changes in oxygen availability (i.e., they’re euryoxic).
- Tracking juvenile horseshoe crabs with your eyes can be a great way to spend time at the beach.

- You can also track horseshoe crabs and other wildlife with your iPhone while at the beach.
- You can get involved in helping stranded horseshoe crabs and ‘Just flip ’em’ (see last picture).
- If you are a classroom teacher in Maryland you can raise horseshoe crabs as a way to increase student’s ocean literacy.
- Monitoring programs, like this one in Long Island Sound, are helping to advance the understanding of horseshoe crabs and their impact on humans.
- Development, pollution, water quality, and over harvesting have impaired the horseshoe crab’s habitat.
- Today and in the future we have the chance to protect horseshoe crab populations at a sustainable level for ecological and commercial uses.
















What people are saying …