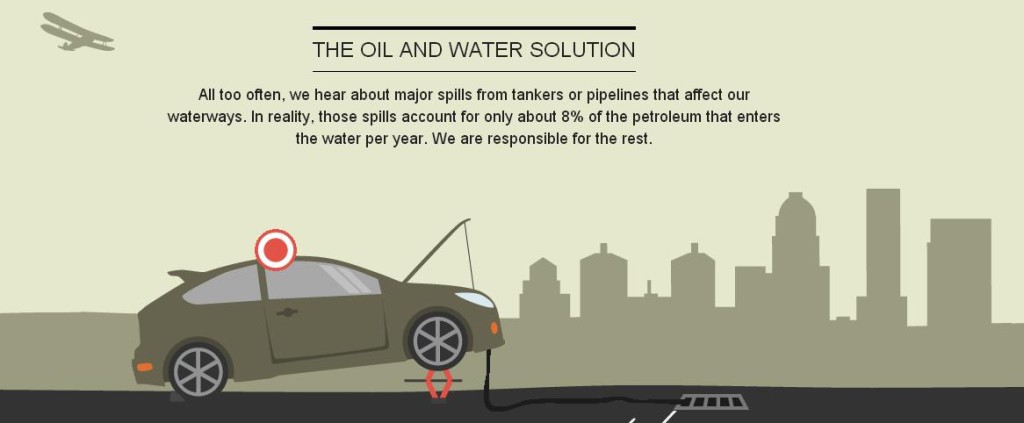
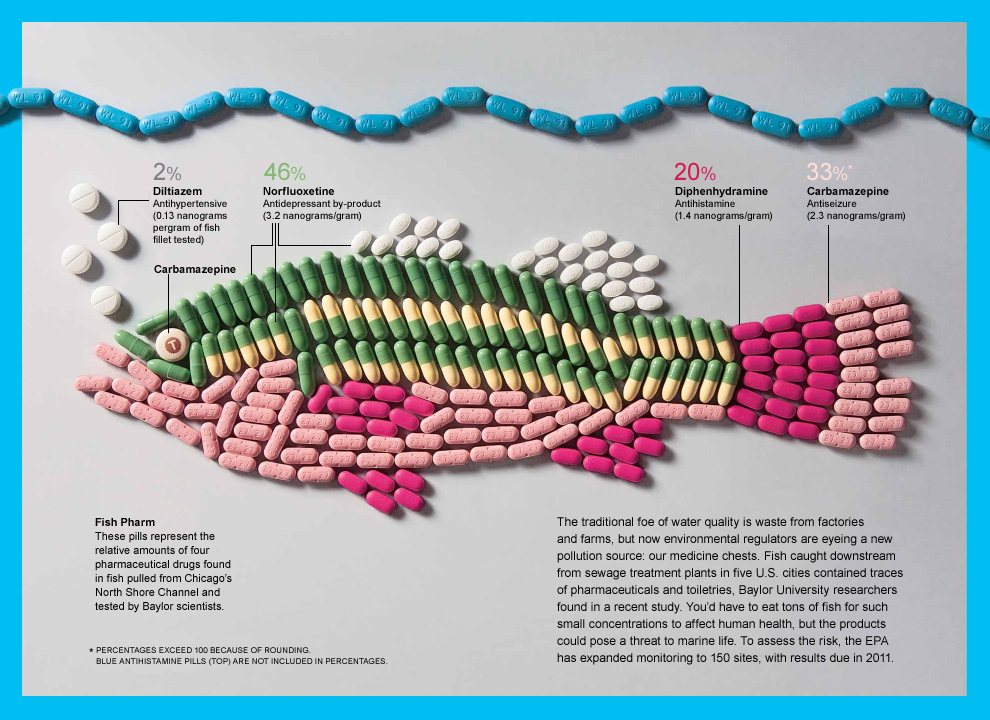
Yesterday I wrote a post about pharmaceuticals affecting aquatic life our waterways and finished it up with a question, “Have you heard of any other ways fish or aquatic life are affected by what we put in our waterways?” Well, I’m too excited to share another culprit. We all know how oil spills affect wildlife because we’ve seen the commercials and very powerful images after a big spill. However, it happens all the time! According to a 2002 report by the National Academies of Science National Research Council petroleum that enters North American waters comes from human activities (e.g., runoff, emissions), not from the ships that transport it. Here’s an image explaining the surprising fact that gas from our cars – not tankers or pipelines – is responsible for 92% of the petroleum spilled into the water. This image is taken from the infographic “The Unfiltered Truth About Water” created by Evergreen AES.
Follow these five tips from the American Boating Association to minimize your impact of petroleum entering the waterways:
- Operate only well maintained boats
- Limit full throttle operation
- Eliminate unnecessary idling
- Follow recommended maintenance schedules
- Eliminate spillage when refueling
- And, I’ll add, carpool or take public transportation when possible
So now, besides petroleum and pharmaceuticals, what are some other ways fish or aquatic life are affected by what we put in our waterways?
Do you love infographics as much as I do? Check out this page with some of my favorites.























What people are saying …