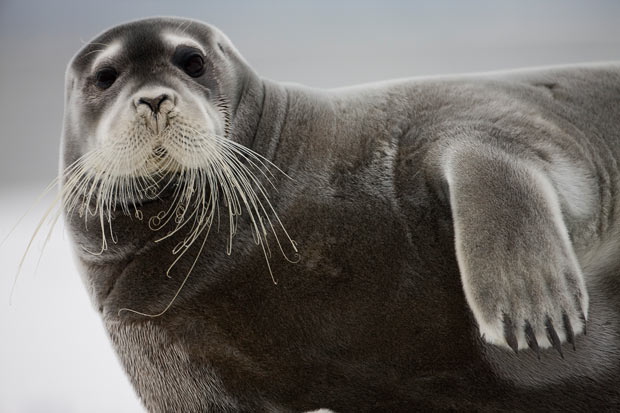
The rather short snout with thick, long, white whiskers gives this true seal it’s appropriate common name. The bearded seal (Erignathus barbatus) can be as long 8 feet and weigh up to 800 pounds. I guess now we know what idiom they use under the sea instead of “the 800 pound gorilla in the room …”. These seals tend not to be seen in packs like their more social counterparts we view along harbors.
Bearded seals spend most of their lives in the Arctic waters, although one was recently found in southeast Florida. They enjoy feasting on arctic cod, shrimp, clams, crabs, and octopus and have been known to live up to 25 years. For more information on the conservation efforts and status of the bearded seal population please check out this page created by the NOAA Fisheries Service Office of Protected Resources.
Image (c) www.telegraph.co.uk















What people are saying …